Social media is the key ingredient of applications and integrating the social media platform with mobile applications the key of success for your mobile applications.
The large social networks could not fit to one single mobile application increasing the opportunity for all mobile developers to create more interesting and creative small apps for mobile devices with this social platforms.
Twitter is one of the popular social networking platform. The update on twitter is very fast as tweets are small in size. Twitter introduced the live streaming APIs to get the updates in real time from twitter live streaming service.
You can integrate the twitter live streaming in your android application as described in this post.
Create a default activity project in eclipse for android and create the following layout for your application in activity_main.xml.
Now replace the default activity class code by the following code
This sample is getting the twitter updates from real time stream API and showing that in a list view. you need to change the username and password values in doInBackGround() method to connect to the twitter.
The following is URL on which we can send a https request to get the tweets update in real time based on the tag value or search keyword.
The AsyncTask is the best way to implement the tweets updates in background. The StreamTask in the sample is extending the AsyncTask and implementing the doInBackGround() method to create a https connection with twitter service and receive a JSON response. The JSON response is parsed by the
handleTweets() method. The method extract the text tweets and add in the hash map to update in the list view.
To update the UI in background function in AsyncTask the publishProgress will send the update to the onProgressUpdate method of AsyncTask.
This call will send a signal to the list view adapter about the change of data and the UI thread update the list view.
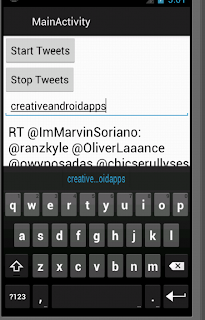
See the output of the sample here
if you like the post then please provide your feedback.
Thanks
Creative Android Apps
The large social networks could not fit to one single mobile application increasing the opportunity for all mobile developers to create more interesting and creative small apps for mobile devices with this social platforms.
Twitter is one of the popular social networking platform. The update on twitter is very fast as tweets are small in size. Twitter introduced the live streaming APIs to get the updates in real time from twitter live streaming service.
You can integrate the twitter live streaming in your android application as described in this post.
Create a default activity project in eclipse for android and create the following layout for your application in activity_main.xml.
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/StartTweetsButton"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="left"
android:text="Start Tweets"
android:onClick="startTweets" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/StopTweetsButton"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="left"
android:text="Stop Tweets"
android:onClick="stopTweets" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/SearchText"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
</EditText>
<ListView android:id="@+id/TweetsList"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
></ListView>
</LinearLayout>
Now replace the default activity class code by the following code
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.URI;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.http.HttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.auth.AuthScope;
import org.apache.http.auth.UsernamePasswordCredentials;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpGet;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.DefaultHttpClient;
import org.json.JSONObject;
import android.os.AsyncTask;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements View.OnClickListener {
private List<HashMap<String,String>> mTweets = new ArrayList<HashMap<String,String>>();
private SimpleAdapter mAdapter;
private boolean m_Running = false;
private String m_SearchKeyWord = "";
final int MAXLIST = 10;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//create a list view and bind with simple adapter
mAdapter = new SimpleAdapter(this, mTweets, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_2, new String[] {"Tweet", "From"}, new int[] {android.R.id.text1, android.R.id.text2});
ListView lv = (ListView)findViewById(R.id.TweetsList);
lv.setAdapter(mAdapter);
//create a list view and bind with simple adapter
}
public class StreamTask extends AsyncTask<Context, Boolean, Boolean> {
protected Boolean doInBackground(Context... arg0) {
try
{
DefaultHttpClient client = new DefaultHttpClient();
String userName = "XXXXXXX";
String password = "XXXXXXX";
UsernamePasswordCredentials creds = new UsernamePasswordCredentials(userName, password);
client.getCredentialsProvider().setCredentials( new AuthScope(AuthScope.ANY_HOST, AuthScope.ANY_PORT), creds);
HttpGet request = new HttpGet();
String m_SearchKeyWord = null;
request.setURI(new URI("https://stream.twitter.com/1/statuses/filter.json?track=" + m_SearchKeyWord));
HttpResponse response = client.execute(request);
InputStream in = response.getEntity().getContent();
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader(in) );
handleTweets(reader);
in.close();
}
catch (Exception e) {
Log.e("SampleTwitter", "doInBackground_" + e.toString());
}
return true;
}
private void handleTweets( BufferedReader reader ) {
try {
String line = "";
do
{
line = reader.readLine();
JSONObject tweet = new JSONObject(line);
HashMap<String, String> tweetMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
if (tweet.has("text")) {
Log.i("SampleTwitter","Tweet : " + tweet.getString("text"));
tweetMap.put("Tweet", tweet.getString("text"));
tweetMap.put("From", tweet.getJSONObject("user") .getString("screen_name"));
Log.i("SampleTwitter","From : " + tweet.getJSONObject("user") .getString("screen_name"));
mTweets.add(0, tweetMap);
if (mTweets.size() > MAXLIST)
{
mTweets.remove(mTweets.size() - 1);
}
publishProgress(true);
}
} while (m_Running && line.length() > 0);
}
catch (Exception e) {
Log.e("SampleTwitter", "handleTweets_" + e.toString());
}
}
protected void onProgressUpdate(Boolean... values) {
super.onProgressUpdate(values);
mAdapter.notifyDataSetChanged();
Log.d("SampleTwitter", "Im in onProgressUpdate()");
}
}
public void stopTweets(View view ) {
m_Running = false;
for(int idx=mTweets.size()-1;idx>=0;idx--)
mTweets.remove(idx);
if(mTweets.size() ==1)
mTweets.remove(0);
mAdapter.notifyDataSetChanged();
}
public void startTweets(View view) {
if( m_Running == false )
{
EditText edt = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.SearchText);
m_SearchKeyWord = edt.getText().toString();
if( m_SearchKeyWord.length() > 0 )
{
StreamTask st = new StreamTask();
st.execute();
m_Running = true;
}
else
{
Toast.makeText(this, "Please enter the search keyword", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
else
{
Toast.makeText(this, "Already Running", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.activity_main, menu);
return true;
}
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}
This sample is getting the twitter updates from real time stream API and showing that in a list view. you need to change the username and password values in doInBackGround() method to connect to the twitter.
The following is URL on which we can send a https request to get the tweets update in real time based on the tag value or search keyword.
https://stream.twitter.com/1/statuses/filter.json?track=?The AsyncTask is the best way to implement the tweets updates in background. The StreamTask in the sample is extending the AsyncTask and implementing the doInBackGround() method to create a https connection with twitter service and receive a JSON response. The JSON response is parsed by the
handleTweets() method. The method extract the text tweets and add in the hash map to update in the list view.
To update the UI in background function in AsyncTask the publishProgress will send the update to the onProgressUpdate method of AsyncTask.
mAdapter.notifyDataSetChanged();This call will send a signal to the list view adapter about the change of data and the UI thread update the list view.
See the output of the sample here
 |
| Twitter Live Streaming |
if you like the post then please provide your feedback.
Thanks
Creative Android Apps
