Android
is a software development stack includes operating system, middleware
technology and application frameworks
Android
is a Linux-based operating system for mobile devices like smart phones and
tablets.
Android
is developed by the Open Handset Alliance. Google purchased the Android from
the initial developer Android Inc. in
year 2005. Google released the Android code as open source under Apache
License.
The
Android stack is divided in four major layers.
Linux Kernel Layer– The core layer of the android
operating system is the Linux kernel. The core layer provides the interface
between hardware layer and software layers. The security, memory management,
user process management, network and driver management is handled at this
layer. The Android is based on Linux kernel 2.6.
Android Runtime and Core Library
Layer – This
Layer provides a Dalvik Virtual Machine and core set of libraries to run the
JAVA applications. The Dalvik VM executes the .dex (Dalvik executable) files.
The Dalvik VM is optimized to run the small footprint of applications at fast
speed.
Each of application runs its own process on Linux kernel and run a
different instance of Dalvik VM.
Android includes a
set of C/ C++ libraries used by various components of the Android Platform. These
libraries could be accessible by developers using standard application
frameworks.
Library
|
Description
|
C
System Library (libc)
|
Optimized
library for embedded Linux devices
|
Media
libraries
|
Libraries to support
playback and recording of many popular audio and video formats, as well as
static image files, including MPEG4, H.264, MP3, AAC, AMR, JPG, and PNG
|
Surface
Manager
|
Manage
access to the display subsystem
|
LibWebCore
|
Web
browser engine to manage the web views
|
SGL
|
2D
graphics engine
|
3D
Libraries
|
OpenGL
ES 1.0 3D libraries for high quality 3D raster graphics
|
Free Type
|
Bitmap
and Vector Font Rendering
|
SQLLite
|
Lightweight
relational database with SQL access
|
Application Framework Layer
– Application Framework Layer provides a set of frameworks to access the
android run-time libraries and core functions to create and manage the user
interface, run background jobs, set notifications and alarms. The components re-usability provides a flexible application development with framework layer.
The application architecture allows the application to publish its features to
other applications.
At high level the
android system provides the following set of system services
·
A rich and extensible set of views used to build
the user interfaces for applications
·
Content Providers to share and access the data
between applications.
·
A Resource Manager to manage the resources
·
A Notification Manager to display the alerts and
notifications on status bar
·
An Activity Manager to manage the lifecycle of
application and state management
The top layer is the application layer where lot of applications are bundled with platform and developers can build their own applications.
See the bellow the Android Architecture Diagram
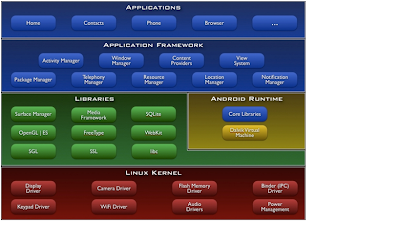 |
| Android Architecture |